NextjsSite
The NextjsSite construct is a higher level CDK construct that lets you create Next.js apps on AWS. It uses OpenNext to build your Next.js app, and transforms the build output to a format that can be deployed to AWS.
Here's how it works at a high level.
- The client assets are deployed to an S3 Bucket, and served out from a CloudFront CDN for fast content delivery.
- The app server and API functions are deployed to Lambda. You can deploy to Lambda@Edge instead if the
edgeflag is enabled. Read more about Single region vs Edge. - You can reference other AWS resources directly in your Next.js app.
- You can configure custom domains.
Quick Start
You can use SST in an existing Next.js app in drop-in mode or inside a monorepo app in standalone mode.
If you have an existing Next.js app, just run
npx create-sstat the root and it'll configure SST in drop-in mode.npx create-sst@latestIf you are starting from scratch, we recommend using our monorepo starter in standalone mode.
npx create-sst@latest --template standard/nextjs
This adds the
NextjsSiteconstruct to your stacks code.import { NextjsSite, StackContext } from "sst/constructs";
export default function MyStack({ stack }: StackContext) {
// ... existing constructs
// Create the Next.js site
const site = new NextjsSite(stack, "Site", {
path: "packages/web",
});
// Add the site's URL to stack output
stack.addOutputs({
URL: site.url,
});
}When you are building your SST app,
NextjsSitewill invokenpx open-next@latest buildinside the Next.js app directory. We also print out thesite.urlonce deployed.We also use the
sst bindcommand in your Next.js app'spackage.jsonto runnext dev. This allows you to bind your AWS resources directly to your Next.js app."scripts": {
- "dev": "next dev",
+ "dev": "sst bind next dev",
"build": "next build",
},
note
If you are using getStaticProps in your app, you'll need to change your build command from next build to sst bind next build. Read more about this below.
Check out the full Next.js tutorial.
Working locally
To work on your Next.js app locally with SST:
Start SST in your project root.
npx sst devThen start your Next.js app. This should run
sst bind next dev.npm run dev
note
When running sst dev, SST does not deploy your Next.js app. It's meant to be run locally.
Single region vs edge
There are two ways you can deploy a Next.js app to your AWS account.
Single region
By default, the Next.js app server is deployed to a single region defined in your
sst.config.tsor passed in via the--regionflag.Edge
Alternatively, you can choose to deploy to the edge. When deployed to the edge, middleware, SSR functions, and API routes are running on edge location that is physically closer to the end user. In this case, the app server is deployed to AWS Lambda@Edge.
const site = new NextjsSite(stack, "Site", {
path: "my-next-app/",
edge: true,
});
Note that, if you have a centralized database, Edge locations are often far away from your database. If you are querying your database in your SSR functions and API routes, you might experience much longer latency when deployed to the edge.
info
If you are not sure which one to use, we recommend deploying to a single region.
Custom domains
You can configure the app with a custom domain hosted either on Route 53 or externally.
const site = new NextjsSite(stack, "Site", {
path: "my-next-app/",
customDomain: "my-app.com",
});
Note that visitors to http:// will be redirected to https://.
You can also configure an alias domain to point to the main domain. For example, to setup www.my-app.com to redirect to my-app.com:
const site = new NextjsSite(stack, "Site", {
path: "my-next-app/",
customDomain: {
domainName: "my-app.com",
domainAlias: "www.my-app.com",
},
});
Using AWS services
SST makes it very easy for your NextjsSite construct to access other resources in your AWS account. Imagine you have an S3 bucket created using the Bucket construct. You can bind it to your Next.js app.
const bucket = new Bucket(stack, "Uploads");
const site = new NextjsSite(stack, "Site", {
path: "packages/web",
bind: [bucket],
});
This will attach the necessary IAM permissions and allow your Next.js app to access the bucket through the typesafe sst/node client.
import { Bucket } from "sst/node/bucket";
export async function getServerSideProps() {
console.log(Bucket.Uploads.bucketName);
}
You can read more about this over on the Resource Binding doc.
Resource binding and SSG
If your app is using getStaticProps and is connecting to resources that've been bound it, you might see an error like this while deploying your app.
Cannot access bound resources. This usually happens if the "sst/node" package is used at build time.
You'll need to wrap your next build command with sst bind next build. This'll allow Next.js to build while having access to your resources.
Client side environment variables
You can also pass in environment variables directly to your client side code.
const bucket = new Bucket(stack, "Bucket");
new NextjsSite(stack, "Site", {
path: "packages/web",
environment: {
NEXT_PUBLIC_BUCKET_NAME: bucket.bucketName,
},
});
Now you can access the bucket's name in your client side code.
console.log(process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_BUCKET_NAME);
In Next.js, only environment variables prefixed with NEXT_PUBLIC_ are available in your client side code. Read more about using environment variables over on the Next.js docs.
You can also read about how this works behind the scenes in SST.
Warming
Server functions may experience performance issues due to Lambda cold starts. SST helps mitigate this by creating an EventBridge scheduled rule to periodically invoke the server function.
new NextjsSite(stack, "Site", {
path: "packages/web",
warm: 20,
});
Setting warm to 20 keeps 20 server function instances active, invoking them every 5 minutes.
Note that warming is currently supported only in regional mode.
Cost
There are three components to the cost:
EventBridge scheduler: $0.00864
Requests cost — 8,640 invocations per month x $1/million = $0.00864Warmer function: $0.145728288
Requests cost — 8,640 invocations per month x $0.2/million = $0.001728
Duration cost — 8,640 invocations per month x 1GB memory x 1s duration x $0.0000166667/GB-second = $0.144000288Server function: $0.0161280288 per warmed instance
Requests cost — 8,640 invocations per month x $0.2/million = $0.001728
Duration cost — 8,640 invocations per month x 1GB memory x 100ms duration x $0.0000166667/GB-second = $0.0144000288
For example, keeping 50 instances of the server function warm will cost approximately $0.96 per month
$0.00864 + $0.145728288 + $0.0161280288 x 50 = $0.960769728
This cost estimate is based on the us-east-1 region pricing and does not consider any free tier benefits.
Logging
By default, Lambda sends all logs to the same AWS CloudWatch log group. This makes it hard to find the request you are looking for.
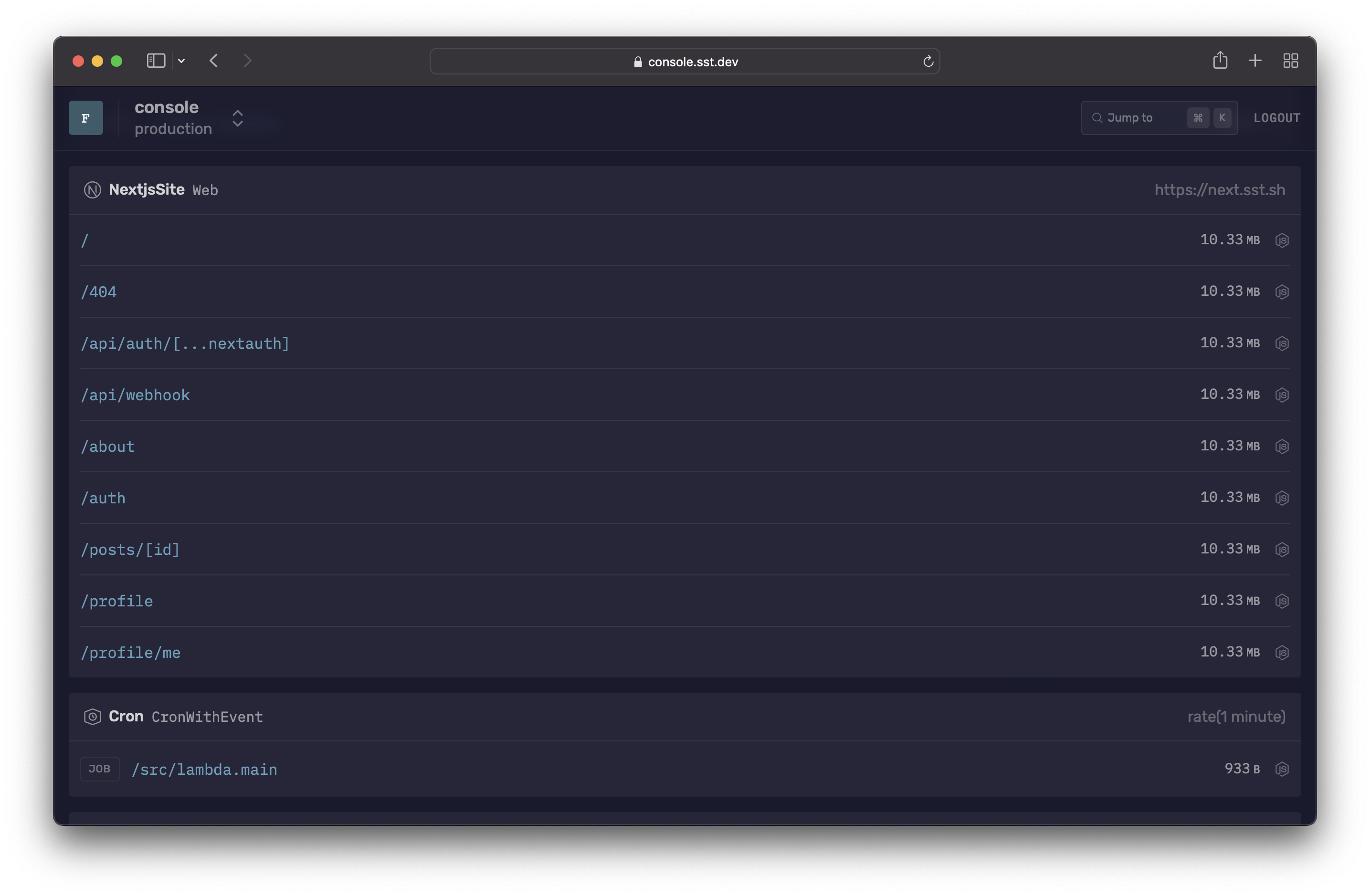
Starting v2.36.0, logs for individual routes are sent to separate log groups. The log group names are prefixed with /sst/lambda, followed by the app server function name, a hash of the route, and ends with route path in a readable format.
/sst/lambda/prod-app-MyNextSite-serverFunction6DFA6F1B-TiNQRV8IhGAu/979bddc4/about
With per-route logging, the SST Console will display all routes within the resources page. To access logs for a specific route, simply select the route from the list.
You can opt-out of this by logging all routes to a single log group by setting the logging prop to combined.
new NextjsSite(stack, "Site", {
path: "my-next-app/",
+ logging: "combined",
});
Source maps
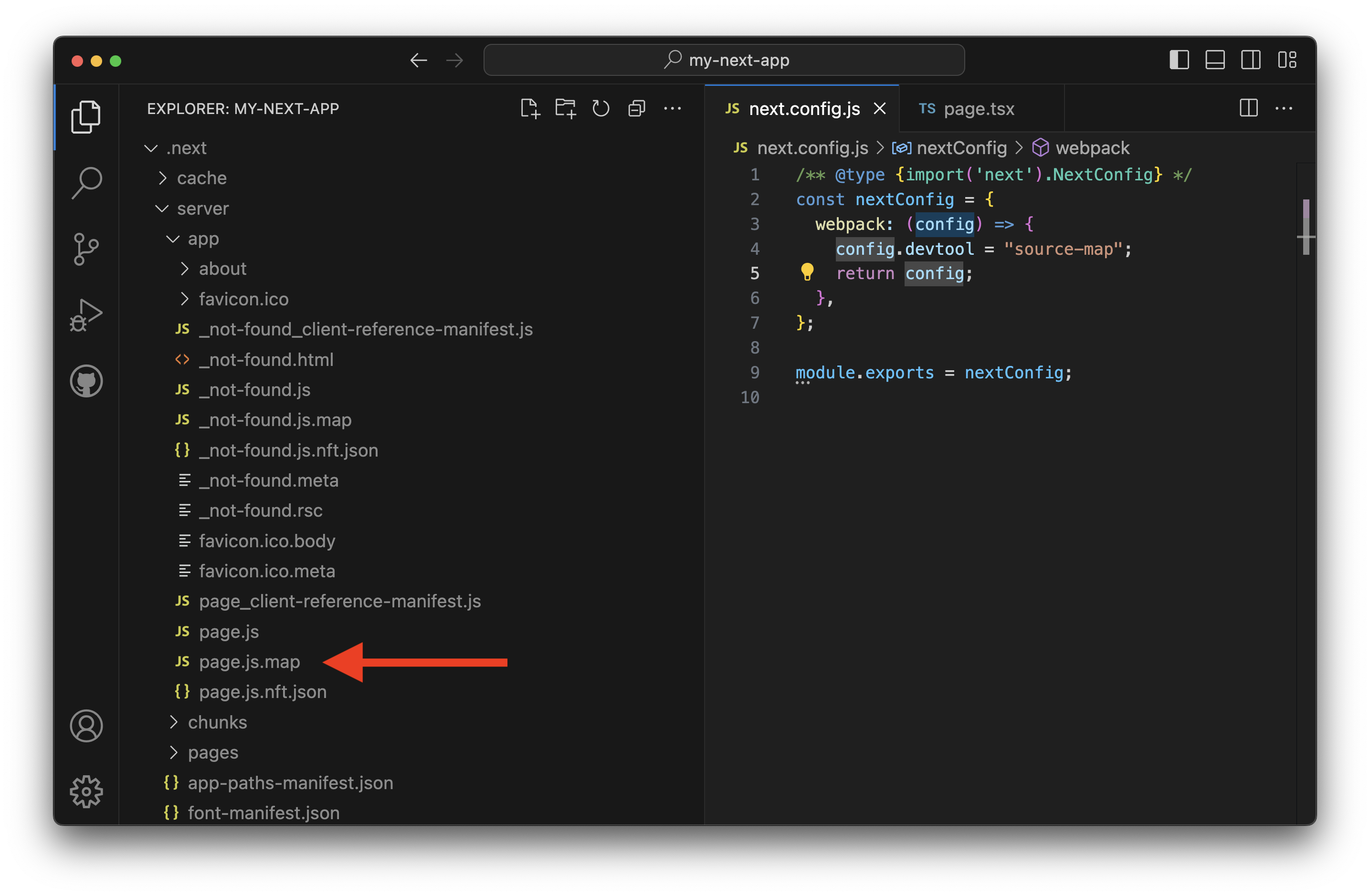
Next.js uses Webpack to bundle your code, so the stack trace line numbers might not match. Turning on sourcemaps when building your Next.js app can fix this.
To enable sourcemaps, make sure you are not disabling per-route logging. Then update your Next.js config:
const nextConfig = {
+ webpack: (config, options) => {
+ if (!options.dev) {
+ config.devtool = "source-map";
+ }
+ return config;
+ },
};
Now when your Next.js app builds, it'll generate the sourcemap files alongside your code. SST uploads these files to the bootstrap bucket.
info
The sourcemap files are not added to the server bundle, keeping the function size small.
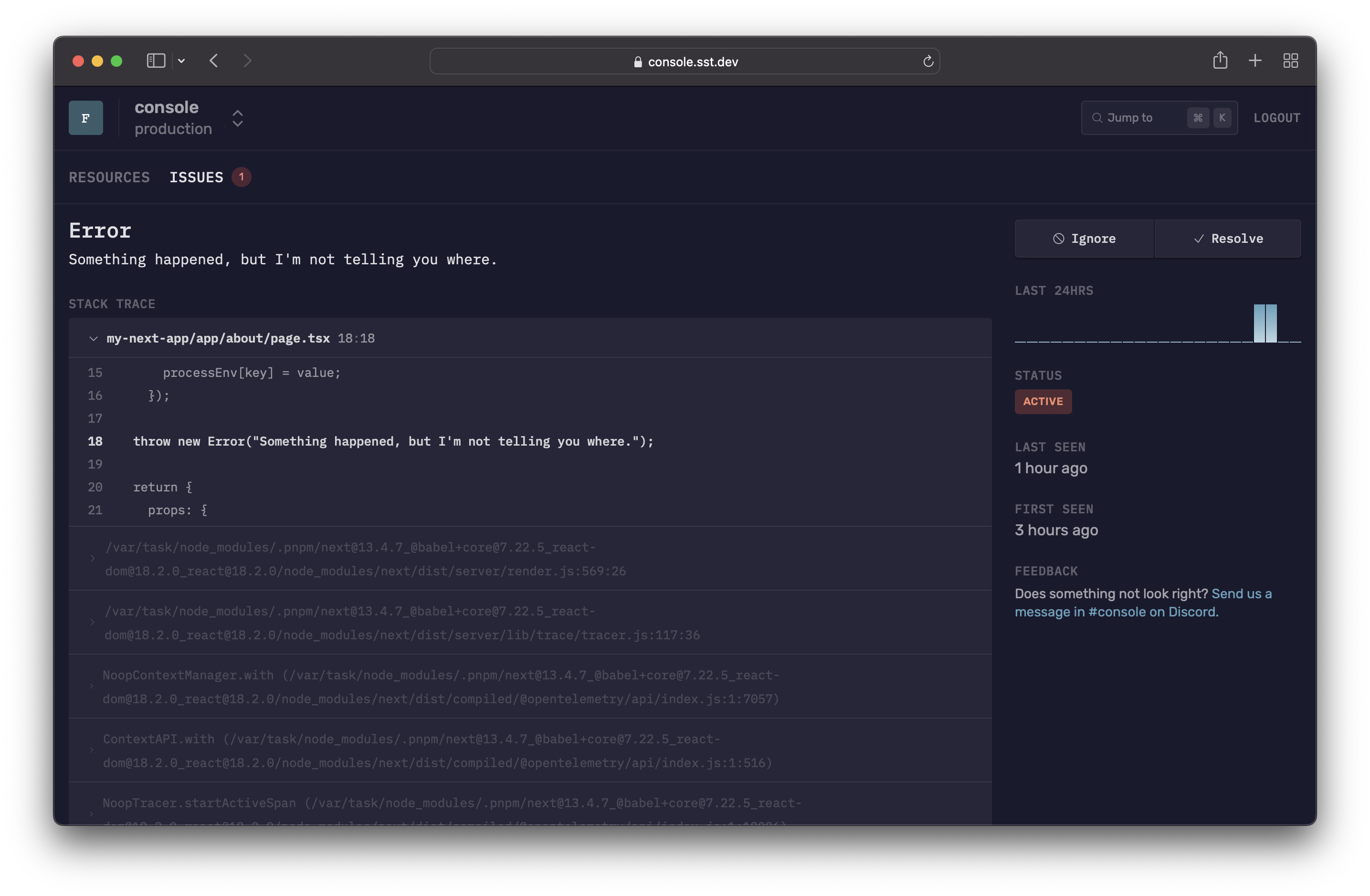
With sourcemaps active, the SST Console will display the errors with the right context.
Examples
Configuring custom domains
You can configure the website with a custom domain hosted either on Route 53 or externally.
Using the basic config (Route 53 domains)
new NextjsSite(stack, "Site", {
path: "my-next-app/",
customDomain: "my-app.com",
});
Redirect www to non-www (Route 53 domains)
new NextjsSite(stack, "Site", {
path: "my-next-app/",
customDomain: {
domainName: "my-app.com",
domainAlias: "www.my-app.com",
},
});
Configuring domains across stages (Route 53 domains)
new NextjsSite(stack, "Site", {
path: "my-next-app/",
customDomain: {
domainName:
stack.stage === "prod" ? "my-app.com" : `${stack.stage}.my-app.com`,
domainAlias: stack.stage === "prod" ? "www.my-app.com" : undefined,
},
});
Configuring alternate domain names (Route 53 domains)
You can specify additional domain names for the site url. Note that the certificate for these names will not be automatically generated, so the certificate option must be specified. Also note that you need to manually create the Route 53 records for the alternate domain names.
import { DnsValidatedCertificate } from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-certificatemanager";
import { HostedZone, RecordTarget, ARecord, AaaaRecord } from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-route53";
import { CloudFrontTarget } from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-route53-targets";
// Look up hosted zone
const hostedZone = HostedZone.fromLookup(stack, "HostedZone", {
domainName: "my-app.com",
});
// Create a certificate with alternate domain names
const certificate = new DnsValidatedCertificate(stack, "Certificate", {
domainName: "foo.my-app.com",
hostedZone,
region: "us-east-1",
subjectAlternativeNames: ["bar.my-app.com"],
});
// Create site
const site = new NextjsSite(stack, "Site", {
path: "my-next-app/",
customDomain: {
domainName: "foo.my-app.com",
alternateNames: ["bar.my-app.com"],
cdk: {
hostedZone,
certificate,
},
},
});
// Create A and AAAA records for the alternate domain names
const recordProps = {
recordName: "bar.my-app.com",
zone: hostedZone,
target: RecordTarget.fromAlias(
new CloudFrontTarget(site.cdk.distribution)
),
};
new ARecord(stack, "AlternateARecord", recordProps);
new AaaaRecord(stack, "AlternateAAAARecord", recordProps);
Importing an existing certificate (Route 53 domains)
import { Certificate } from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-certificatemanager";
new NextjsSite(stack, "Site", {
path: "my-next-app/",
customDomain: {
domainName: "my-app.com",
cdk: {
certificate: Certificate.fromCertificateArn(stack, "MyCert", certArn),
},
},
});
Note that, the certificate needs be created in the us-east-1(N. Virginia) region as required by AWS CloudFront.
Specifying a hosted zone (Route 53 domains)
If you have multiple hosted zones for a given domain, you can choose the one you want to use to configure the domain.
import { HostedZone } from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-route53";
new NextjsSite(stack, "Site", {
path: "my-next-app/",
customDomain: {
domainName: "my-app.com",
cdk: {
hostedZone: HostedZone.fromHostedZoneAttributes(stack, "MyZone", {
hostedZoneId,
zoneName,
}),
},
},
});
Configuring externally hosted domain
import { Certificate } from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-certificatemanager";
new NextjsSite(stack, "Site", {
path: "my-next-app/",
customDomain: {
isExternalDomain: true,
domainName: "my-app.com",
cdk: {
certificate: Certificate.fromCertificateArn(stack, "MyCert", certArn),
},
},
});
Note that the certificate needs be created in the us-east-1(N. Virginia) region as required by AWS CloudFront, and validated. After the Distribution has been created, create a CNAME DNS record for your domain name with the Distribution's URL as the value. Here are more details on configuring SSL Certificate on externally hosted domains.
Also note that you can also migrate externally hosted domains to Route 53 by following this guide.
Configuring server function
new NextjsSite(stack, "Site", {
path: "my-next-app/",
timeout: "5 seconds",
memorySize: "2048 MB",
});
Configuring image optimization function
new NextjsSite(stack, "Site", {
path: "my-next-app/",
imageOptimization: {
memorySize: "2048 MB",
},
});
Advanced examples
Configuring basic auth
The following example demonstrates how to inject code for Basic Authentication validation into CloudFront functions.
new NextjsSite(stack, "Site", {
path: "my-next-app/",
cdk: {
transform: (plan) => {
const username = "admin";
const password = "P@ssw0rd!";
const basicAuth = Buffer.from(`${username}:${password}`).toString("base64");
plan.cloudFrontFunctions.serverCfFunction.injections.push(`
if (request?.headers?.authorization?.value !== 'Basic ${basicAuth}') {
return {
statusCode: 401,
statusDescription: "Unauthorized",
headers: {
"www-authenticate": { value: 'Basic realm="Secure Area"' },
},
};
}
`);
},
},
});
Ensure that the username and password variables are set to your desired credentials. This script will intercept incoming requests and check for a valid Basic Authentication header. If the header is missing or incorrect, the response will be a 401 Unauthorized status with a prompt for authentication.
Configuring VPC
Note that VPC is only supported when deploying to a single region.
import { Vpc, SubnetType } from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-ec2";
// Create a VPC
const vpc = new Vpc(stack, "myVPC");
// Alternatively use an existing VPC
const vpc = Vpc.fromLookup(stack, "myVPC", { ... });
const vpcSubnets = {
subnetType: SubnetType.PRIVATE_WITH_EGRESS,
};
new NextjsSite(stack, "Site", {
path: "my-next-app/",
cdk: {
server: {
vpc,
vpcSubnets,
},
revalidation: {
vpc,
vpcSubnets,
}
}
});
Configuring log retention
import { RetentionDays } from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-logs";
new NextjsSite(stack, "Site", {
path: "my-next-app/",
cdk: {
server: {
logRetention: RetentionDays.ONE_MONTH,
}
},
});
Using an existing S3 Bucket
import { Bucket } from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-s3";
import { OriginAccessIdentity } from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-cloudfront";
new NextjsSite(stack, "Site", {
path: "my-next-app/",
cdk: {
bucket: Bucket.fromBucketName(stack, "Bucket", "my-bucket"),
// Required for non-public buckets
s3Origin: {
originAccessIdentity: OriginAccessIdentity.fromOriginAccessIdentityId(
stack,
"OriginAccessIdentity",
"XXXXXXXX"
),
},
},
});
Setting the originAccessIdentity prop enables an imported bucket to be properly secured with a bucket policy without giving public access to the bucket.
Reusing CloudFront cache policies
CloudFront has a limit of 20 cache policies per AWS account. This is a hard limit, and cannot be increased. If you plan to deploy multiple Next.js sites, you can have the constructs share the same cache policies by reusing them across sites.
import { Duration } from "aws-cdk-lib";
import {
CachePolicy,
CacheQueryStringBehavior,
CacheHeaderBehavior,
CacheCookieBehavior,
} from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-cloudfront";
const serverCachePolicy = new CachePolicy(stack, "ServerCache", NextjsSite.buildDefaultServerCachePolicyProps());
new NextjsSite(stack, "Site1", {
path: "my-next-app/",
cdk: {
serverCachePolicy,
},
});
new NextjsSite(stack, "Site2", {
path: "another-next-app/",
cdk: {
serverCachePolicy,
},
});
Configuring CloudFront response headers policies
import { ResponseHeadersPolicy } from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-cloudfront";
new NextjsSite(stack, "Site", {
path: "my-next-app/",
cdk: {
responseHeadersPolicy: ResponseHeadersPolicy.CORS_ALLOW_ALL_ORIGINS,
},
});
Enabling HTTP/3 support
import { HttpVersion } from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-cloudfront";
new NextjsSite(stack, "Site", {
path: "my-next-app/",
cdk: {
distribution: {
httpVersion: HttpVersion.HTTP3,
},
},
});
Common Issues
Next.js app built twice
When running sst build or sst deploy, you might notice the Next.js app building twice. This often occurs if you've configured custom domains or VPC within your NextjsSite construct or elsewhere in your app.
SST (AWS CDK) may need to look up specific details from the AWS account where the app is deployed. For instance, SST looks up the Route 53 hosted zone data for a custom domain; and fetches AWS region details when referencing an existing VPC. SST stores these details in cdk.context.json.
If cdk.context.json file is absent, SST builds the app, generates the cdk.context.json file, and then builds again.
To avoid building the Next.js app twice, ensure the cdk.context.json file is committed to your git repository.
Likewise, if the app builds twice in your CI environment, commit any modifications to cdk.context.json.
Constructor
new NextjsSite(scope, id, props)
Parameters
- scope Construct
- id string
- props NextjsSiteProps
NextjsSiteProps
assets?
Type :
assets.fileOptions?
Type : Array<SsrSiteFileOptions>
List of file options to specify cache control and content type for cached files. These file options are appended to the default file options so it's possible to override the default file options by specifying an overlapping file pattern.
assets: {
fileOptions: [
{
files: "**/*.zip",
cacheControl: "private,no-cache,no-store,must-revalidate",
contentType: "application/zip",
},
],
}
assets.nonVersionedFilesCacheHeader?
Type : string
Default : public,max-age=0,s-maxage=86400,stale-while-revalidate=8640
The header to use for non-versioned files (ex:
index.html
) in the CDN cache. When specified, the
nonVersionedFilesTTL
option is ignored.
assets: {
nonVersionedFilesCacheHeader: "public,max-age=0,no-cache"
}
assets.nonVersionedFilesTTL?
Type : number | ${number} second | ${number} seconds | ${number} minute | ${number} minutes | ${number} hour | ${number} hours | ${number} day | ${number} days
Default : 1 day
The TTL for non-versioned files (ex:
index.html
) in the CDN cache. Ignored when
nonVersionedFilesCacheHeader
is specified.
assets: {
nonVersionedFilesTTL: "4 hours"
}
assets.textEncoding?
Type : "ascii" | "utf-8" | "none" | "iso-8859-1" | "windows-1252"
Default : utf-8
Character encoding for text based assets uploaded to S3 (ex: html, css, js, etc.). If "none" is specified, no charset will be returned in header.
assets: {
textEncoding: "iso-8859-1"
}
assets.versionedFilesCacheHeader?
Type : string
Default : public,max-age=31536000,immutable
The header to use for versioned files (ex:
main-1234.css
) in the CDN cache. When specified, the
versionedFilesTTL
option is ignored.
assets: {
versionedFilesCacheHeader: "public,max-age=31536000,immutable"
}
assets.versionedFilesTTL?
Type : number | ${number} second | ${number} seconds | ${number} minute | ${number} minutes | ${number} hour | ${number} hours | ${number} day | ${number} days
Default : 1 year
The TTL for versioned files (ex:
main-1234.css
) in the CDN and browser cache. Ignored when
versionedFilesCacheHeader
is specified.
assets: {
versionedFilesTTL: "30 days"
}
bind?
Type : Array<BindingResource>
Bind resources for the function
new Function(stack, "Function", {
handler: "src/function.handler",
bind: [STRIPE_KEY, bucket],
})
buildCommand?
Type : string
Default : npm run build
The command for building the website
buildCommand: "yarn build",
customDomain?
Type : string | SsrDomainProps
The customDomain for this website. SST supports domains that are hosted either on Route 53 or externally.
Note that you can also migrate externally hosted domains to Route 53 by following this guide.
customDomain: "domain.com",
customDomain: {
domainName: "domain.com",
domainAlias: "www.domain.com",
hostedZone: "domain.com"
},
dev?
Type :
dev.deploy?
Type : boolean
Default : false
When running
sst dev
, site is not deployed. This is to ensure
sst dev
can start up quickly.
dev: {
deploy: true
}
dev.url?
Type : string
The local site URL when running
sst dev
.
dev: {
url: "http://localhost:3000"
}
edge?
Type : boolean
Default : false
The server function is deployed to Lambda in a single region. Alternatively, you can enable this option to deploy to Lambda@Edge.
environment?
Type : Record<string, string>
An object with the key being the environment variable name.
environment: {
API_URL: api.url,
USER_POOL_CLIENT: auth.cognitoUserPoolClient.userPoolClientId,
},
imageOptimization?
Type :
imageOptimization.memorySize?
Type : number | ${number} MB | ${number} GB
Default : 1024 MB
The amount of memory in MB allocated for image optimization function.
imageOptimization: {
memorySize: "512 MB",
}
imageOptimization.staticImageOptimization?
Type : boolean
Default : false
If set to true, already computed image will return 304 Not Modified. This means that image needs to be immutable, the etag will be computed based on the image href, format and width and the next BUILD_ID.
imageOptimization: {
staticImageOptimization: true,
}
### invalidation?
_Type_ :
### invalidation.paths?
_Type_ : <span class='mono'>Array<<span class="mono">string</span>></span><span class='mono'> | </span><span class="mono">"none"</span><span class='mono'> | </span><span class="mono">"all"</span><span class='mono'> | </span><span class="mono">"versioned"</span>
_Default_ : <span class="mono">"all"</span>
The paths to invalidate. There are three built-in options:
- "none" - No invalidation will be performed.
- "all" - All files will be invalidated when any file changes.
- "versioned" - Only versioned files will be invalidated when versioned files change.
Alternatively you can pass in an array of paths to invalidate.
Disable invalidation:
```js
invalidation: {
paths: "none",
}
Invalidate "index.html" and all files under the "products" route:
invalidation: {
paths: ["/index.html", "/products/*"],
}
invalidation.wait?
Type : boolean
Default : false
While deploying, SST waits for the CloudFront cache invalidation process to finish. This ensures that the new content will be served once the deploy command finishes. However, this process can sometimes take more than 5 mins. For non-prod environments it might make sense to pass in
false
. That'll skip waiting for the cache to invalidate and speed up the deploy process.
invalidation: {
wait: true,
}
memorySize?
Type : number | ${number} MB | ${number} GB
Default : 1024 MB
The amount of memory in MB allocated for SSR function.
memorySize: "512 MB",
openNextVersion?
Type : string
Default : Latest OpenNext version
OpenNext version for building the Next.js site.
openNextVersion: "2.2.4",
path?
Type : string
Default : "."
Path to the directory where the app is located.
permissions?
Type : Permissions
Attaches the given list of permissions to the SSR function. Configuring this property is equivalent to calling
attachPermissions()
after the site is created.
permissions: ["ses"]
regional?
Type :
regional.enableServerUrlIamAuth?
Type : boolean
Default : false
Secure the server function URL using AWS IAM authentication. By default, the server function URL is publicly accessible. When this flag is enabled, the server function URL will require IAM authorization, and a Lambda@Edge function will sign the requests. Be aware that this introduces added latency to the requests.
regional.prefetchSecrets?
Type : boolean
Default : false
Prefetches bound secret values and injects them into the function's environment variables.
runtime?
Type : "nodejs16.x" | "nodejs18.x" | "nodejs20.x"
Default : nodejs18.x
The runtime environment for the SSR function.
runtime: "nodejs20.x",
timeout?
Type : number | ${number} second | ${number} seconds | ${number} minute | ${number} minutes | ${number} hour | ${number} hours | ${number} day | ${number} days
Default : 10 seconds
The execution timeout in seconds for SSR function.
timeout: "5 seconds",
typesPath?
Type : string
Default : "."
Path relative to the app location where the type definitions are located.
waitForInvalidation?
Type : boolean
Default : false
While deploying, SST waits for the CloudFront cache invalidation process to finish. This ensures that the new content will be served once the deploy command finishes. However, this process can sometimes take more than 5 mins. For non-prod environments it might make sense to pass in
false
. That'll skip waiting for the cache to invalidate and speed up the deploy process.
Use
invalidation.wait
instead.
warm?
Type : number
Default : Server function is not kept warm
The number of server functions to keep warm. This option is only supported for the regional mode.
cdk?
Type :
Properties
An instance of NextjsSite has the following properties.
customDomainUrl
Type : undefined | string
If the custom domain is enabled, this is the URL of the website with the custom domain.
id
Type : string
url
Type : undefined | string
The CloudFront URL of the website.
cdk
Type : undefined |
cdk.bucket
Type : Bucket
cdk.certificate
Type : undefined | ICertificate
cdk.distribution
Type : IDistribution
cdk.function
Type : undefined | IFunction | Function
cdk.hostedZone
Type : undefined | IHostedZone
The internally created CDK resources.
Methods
An instance of NextjsSite has the following methods.
attachPermissions
attachPermissions(permissions)
Parameters
- permissions Permissions
Attaches the given list of permissions to allow the server side rendering framework to access other AWS resources.
site.attachPermissions(["sns"]);
getConstructMetadata
getConstructMetadata()